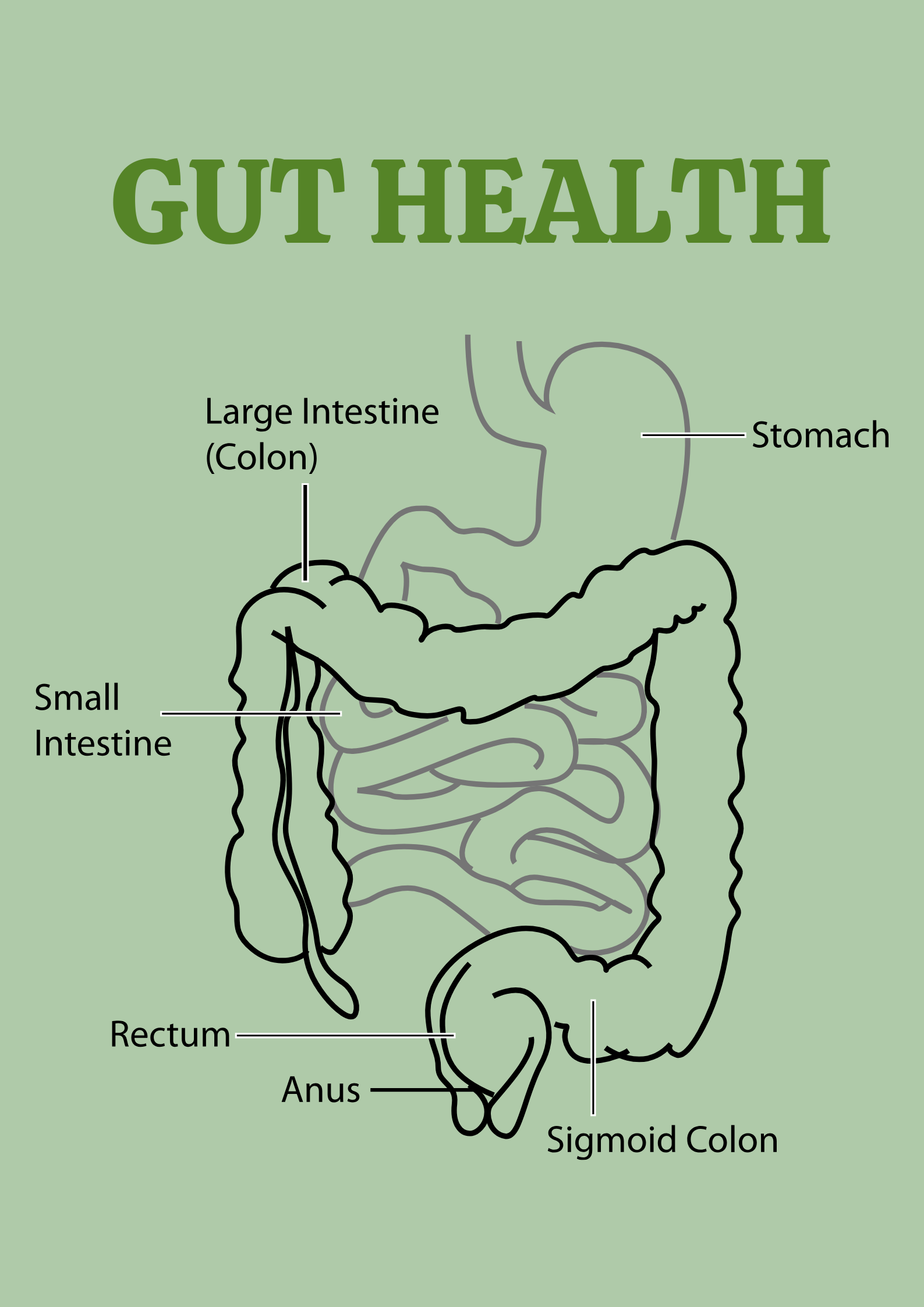
Ever feel bloated after meals? Struggle with low energy or mood swings?
The answer might lie in your gut. Trillions of microbes in your digestive system control everything from digestion to mental health—and fixing your gut could be the key to feeling better naturally.
I’ve seen firsthand how small changes in diet and lifestyle can transform health. The best part? You don’t need expensive supplements or extreme diets. Here’s a simple, science-backed guide to heal your gut and boost your overall well-being.
Your Gut: A Tiny Universe That Controls Your Health
Think of your gut like a thriving garden. For it to flourish, it needs a balance of good bacteria, fiber, and nutrients just like plants need sunlight and water.
Why Your Gut Microbiome Matters
- Digestion & Nutrient Absorption
- Breaks down food, reduces bloating, and helps absorb vitamins (like B12 and K).
- Your Immune System’s Command Center
- 70% of your immune cells live in your gut. A healthy microbiome = fewer infections.
- Defense Against Harmful Bugs
- Good bacteria crowd out bad ones, preventing issues like leaky gut (when toxins sneak into your bloodstream).
How Your Gut Health Affects Your Whole Body
An unhealthy gut doesn’t just cause stomach issues, it’s linked to chronic diseases:
1.Weight & Metabolism
- Low gut bacteria diversity is tied to obesity (some microbes extract more calories from food!).
2. Heart Health
- Certain gut bacteria produce TMAO, a compound linked to heart disease.
3. Type 2 Diabetes
- Imbalanced bacteria can worsen insulin resistance.
4. Autoimmune Conditions
- Leaky gut may trigger IBD, Hashimoto’s, and rheumatoid arthritis.
5. Mood & Brain Health
- 90% of serotonin (your “happy hormone”) is made in the gut.
- Poor gut health is linked to anxiety, depression, and even Alzheimer’s.
7 Warning Signs Your Gut Needs Help
How do you know if your gut is out of balance? Watch for:
- Bloating, gas, or constipation
- Food intolerances (suddenly can’t handle dairy or gluten?)
- Constant colds or weak immunity
- Fatigue, even after good sleep
- Skin issues (acne, eczema, rashes)
- Mood swings, anxiety, or depression
- Brain fog or poor memory
Heal Your Gut Naturally: 8 Science-Backed Tips
1. Eat More Gut-Friendly Foods
probiotics (yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut) add good bacteria.
prebiotics (onions, garlic, garlic, onions, bananas, asparagus) feed good bacteria.
fiber (whole grains, veggies, flaxseeds) keeps digestion smooth.
2. Ditch Sugar & Processed Junk
Sugar feeds harmful bacteria (like Candida).
Artificial sweeteners wreck your microbiome.
3. Stay Hydrated
Water supports digestion and nutrient absorption.
4. Manage Stress
Chronic stress kills good gut bacteria. Try:
- 10-minute walks
- Deep breathing
- Journaling
5. Prioritize Sleep
Poor sleep is linked to more inflammation & worse gut health.
6. Avoid Unnecessary Antibiotics
They wipe out both good and bad bacteria.
7. Move Daily
Exercise boosts microbiome diversity.
8. Try Supplements (If Needed)
Probiotics, prebiotics, omega-3s, and L-glutamine can help repair gut lining.
Final Thought: Small Changes, Big Results
You don’t need a complete lifestyle overhaul start with one change:
- Swap soda for kombucha.
- Add a daily probiotic.
- Take a 5-minute stress break.
Your gut is the foundation of your health. Nourish it, and your whole body will thank you.
Your future self will thank you.
References
- Gut-Brain Connection:
Harvard Health Publishing. (2023). The gut-brain connection. Harvard Medical School. - Gut Microbiome Overview:
Cleveland Clinic. (2024). Gut microbiome. - Microbiome & Chronic Disease:
Lynch, S. V., & Pedersen, O. (2016). The human intestinal microbiome in health and disease. New England Journal of Medicine, 375(24), 2369-2379. - Probiotics/Prebiotics:
National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. (2022). Probiotics: What you need to know. - Leaky Gut Research:
Fasano, A. (2020). All disease begins in the (leaky) gut: Role of zonulin-mediated gut permeability. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 85, 1-4.